THE SHAPE OF IDEAS: THE PROTOTYPE MADE OF MINERALS, BETWEEN CREATION AND REALIZATION
Imagining a model, a shape, a function, a color is an exercise that directly follows creative activities. Creative professionals have the privilege of often going through that extraordinary process with which we visualize a perfectly defined image in our mind. However, they must also think about how to make it real: production, materials, how to highlight the details and all the other elements that make up the manufacturing process.
Imagining for work therefore does not allow us to be satisfied with the only fantastic representation of what is imagined. It is also necessary to plan, to equip the object with the desired quality and performance characteristics. Another fundamental element to plan is related to the time required for implementation.
The first materialization of the idea of a product is drawing. This is the first stage of the realization process which has always been carried out through the use of the best techniques available at the moment: from stone to coal, from primitive tools to drawing on paper.

Anonymous, Headless Statue of Gudea, c. 2130 BC.
|
Renzo Piano, The Shard, 2004.
|
Technology has evolved and, particularly in recent years, offers a series of tools that have become an indispensable aid in representing the idea and in carrying out the activities that precede the placing on the market of a product.
To best represent the idea we make use of Rendering tools: they allow the realistic visualization of projects and objects, even in 3 Dimensions.
The stage following realistic visualization is the creation of a preliminary version of the imagined object. It is one of the activities that are usually entrusted to professionals or specialized companies: that relating to prototyping.
Prototyping is the activity, between concept and production, that allows you to determine if the imagined object (or project) can be transformed into reality. The result of such an important activity is the prototype.
Stone 3D printed.
What is a prototype?
A prototype is, in short, a preliminary version of an object. It is the physical representation of a vision but not yet a finished product. During the process that preludes the placing on the market of an object or the realization of a project, there are several stages in which a prototype allows you to benefit from its usefulness. In fact, the prototypes perform their very important function allowing to refine, according to the specific objectives of each company operating area, all the different development phases: performance tests, economic evaluation (both cost and revenue), marketing, tests and research market, physical production (difficulties and timing), etc. Activities that cannot be performed without an actual physical realization of the object / project even if represented realistically with a render.
There are in fact different types of prototypes whose characteristics vary according to the development phase in which they are made:
Appearance prototype: must not contain specific details or functionality; they may not even be made with the production materials, usually more expensive. Appearance prototypes are made in the early stages of the process and their purpose is exclusively to physically represent the object. They also allow to carry out tests and market research, presenting them to potential customers and asking them for feedback on different characteristics: aesthetics, dimensions, sale price, utility, etc …
This type of prototype cannot be subjected to physical or functional tests, but allows other very important uses. An appearance prototype can, for example, be used for market research: companies can present their similar prototype to potential customers, asking them for an opinion on the appearance of the product (or on aesthetic or dimensional details, for example) and to contribute to the definition of the best characteristics.
Functional prototype: it is more than just a physical representation but it is still different from the final version of the product. The functional prototype is used to experiment and validate the use of some specific functions of the imagined object / project. Specific tests will be carried out on the prototype to ascertain whether the product will be suitable for the intended use. During the verifications, the results obtained suggest mostly adaptations but may also suggest new features and / or new opportunities for using the product.
Pre-production prototype: while appearance prototypes and functional prototypes are generally made in the early stages of the development process, pre-production prototypes are made, as the name indicates, when all the previous stages are almost completed, the final version has been defined and the product must be placed on the market.
This type of prototype allows to optimize, verify and standardize production processes and flows. In this phase, Creatives hardly ever participate, who give way to production managers. This kind of prototype is usually made with the final materials, those of production. They contain all the aesthetic, dimensional, performance details and all the functionality of the finished product. However, they do not go on the market. They are also almost always used to make the technical data sheets and acquire the certifications necessary for placing the product on the market.
What are the additional benefits that make prototypes so important?
There are still several advantages that make them precious and irreplaceable and there are further functions of the prototypes that we briefly describe:
- they help to describe and confirm the value of the product, demonstrating its appearance and functionality;
- they increase the effectiveness of a presentation because they allow you to physically “touch” the product;
- they allow accurate studies, tests, inspections and development activities increasing the effectiveness of the results;
- they give the opportunity to present an idea, express new concepts, to propose new styles, new materials, new features;
- they allow to easily analyze different conceptual proposals, physically comparing prototypes that contain different characteristics, details, materials, functions.
Further advantages of the prototypes can be indicated for specific product sectors.
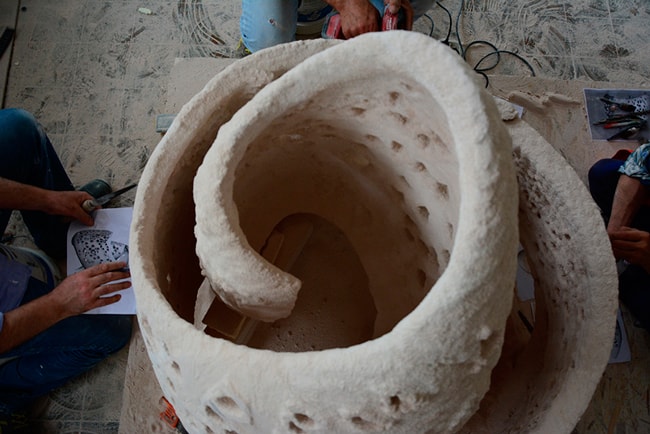
Tests carried out according to the 3D printing of the VHT prototype, i.e. the Venetian Heritage Tower.
The completed work is exhibited at the Marghera tower.
How is a prototype made?
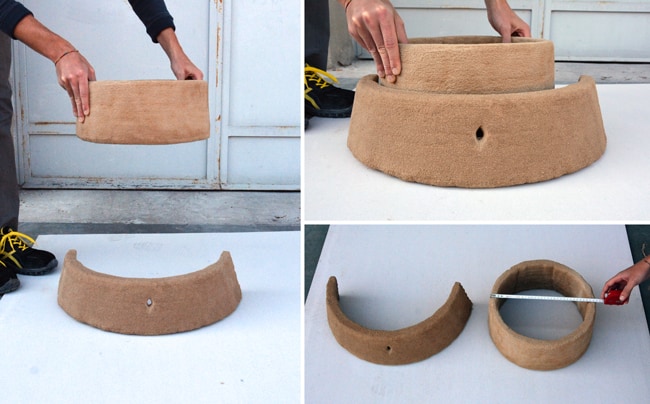
The method of making a prototype takes on a fundamental aspect depending on the phase of the product development in which it is made. And of the life phase (cycle) of the imagined product (introduction of an innovative product, new family, new version, series, etc.). As we have seen, the prototype also serves to define the most efficient production process: in this case (pre-production) the production methods will reflect processes studied to be repeated, constantly guaranteeing the same quality. Structured companies have internal areas dedicated to prototyping, equipped with different technologies. Less structured companies usually rely on specialized companies that offer this service.
However, there are needs common to all companies and to the different phases of product development which make it preferable to choose one or the other company or the technique and / or technology to be used for the realization of the prototype: the two most important are production times and costs. While the former are not decisive if they are proportional to the quantity and quality of the prototypes, reducing the time for placing a product on the market has become an essential, fundamental element of competitiveness.
The technology offers, also in this case, a valid help: the use of the Additive Manufacturing (or 3D printing) to make the prototypes.
There are many advantages that this production technology offers. Especially for the realization of prototypes and in all phases of product development.
Printing in 3D is simpler than you think: just create a digital model that respects some simple rules, and send it to print. Production times depend on the size of the object and the material chosen to produce it: in any case, a few days.
Even if the object has large dimensions (greater than 500 mm), a 3D prototype can be made. And even if the material chosen for the production is a mineral: marble, stones, sand, etc.
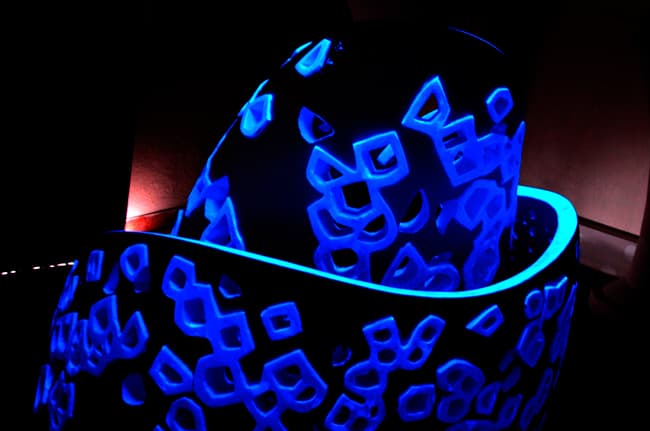
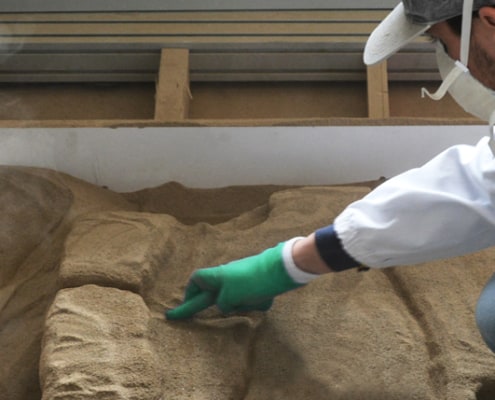
Desamanera is specialized in large scale Additive Manufacturing, made with minerals and natural binders. It offers 3D printing service with proprietary technologies to customers all over the world. And that’s not all: it has developed an artisanal process which process minerals to create unique, exclusive and customizable professional finishes. This is a complementary service to 3D printing of minerals because it has an extreme aesthetic versatility and allows a very wide customization of the aesthetic characteristics. We have already talked about MarbleSkin™ in this article and this is its official page.
This process also respects the stringent environmental and ecological production characteristics with which Desamanera characterizes its products.
Desamanera knows and enhances the importance of the service and it is in its mission to help customers who do not yet know it to get the most out of the service offered to them.
Not sure where to start? Request the brochure and take the first step towards the large prototype you need; you will also find out how to customize, exclusively with minerals, all your products.
Published on 7th April 2020










